| AA | Aa | aa | Total | |
| Cases | r0 | r1 | r2 | R |
| Controls | s0 | s1 | s2 | S |
| Total | n0 | n1 | n2 | N |
ISSN 0253-2778
CN 34-1054/N
The three common genetic models (or modes of inheritance) in association analysis are the dominant, additive, and recessive models. It is known that the Cochran-Armitage trend test (CATT) which correctly incorporates information from genetic models, is more powerful than the commonly used Pearson’s chi-square test. However, the true genetic model is usually unknown in practice, and the power of the CAT test could be substantially reduced with a wrongly specified genetic model. To achieve a power that is close to that of a correctly specified CAT test, it is natural to apply trend tests under different possible genetic models and to report the most significant test result. This results in a MAX-type testing procedure, and it was found that this test is usually more powerful than the Pearson’s chi-square test. Although the significance (i.e., p value) of the MAX-type test can be accessed by either large sample approximation or permutation methods, requirements for sample size or simulation replicates are demanding with respect to accuracy and efficiency. This paper proposes an approach to calculate the exact p values of MAX-type tests based on the combinatorial counting method. The simulation results show that the exact method is more accurate than the large sample approximation methods and more computationally efficient than the permutation method, and our method can be readily applied to genome-wide association studies (GWASs). The proposed method is built in an R package, MaXact, which is available at the https://github.com/Myuan2019/MaXact/.
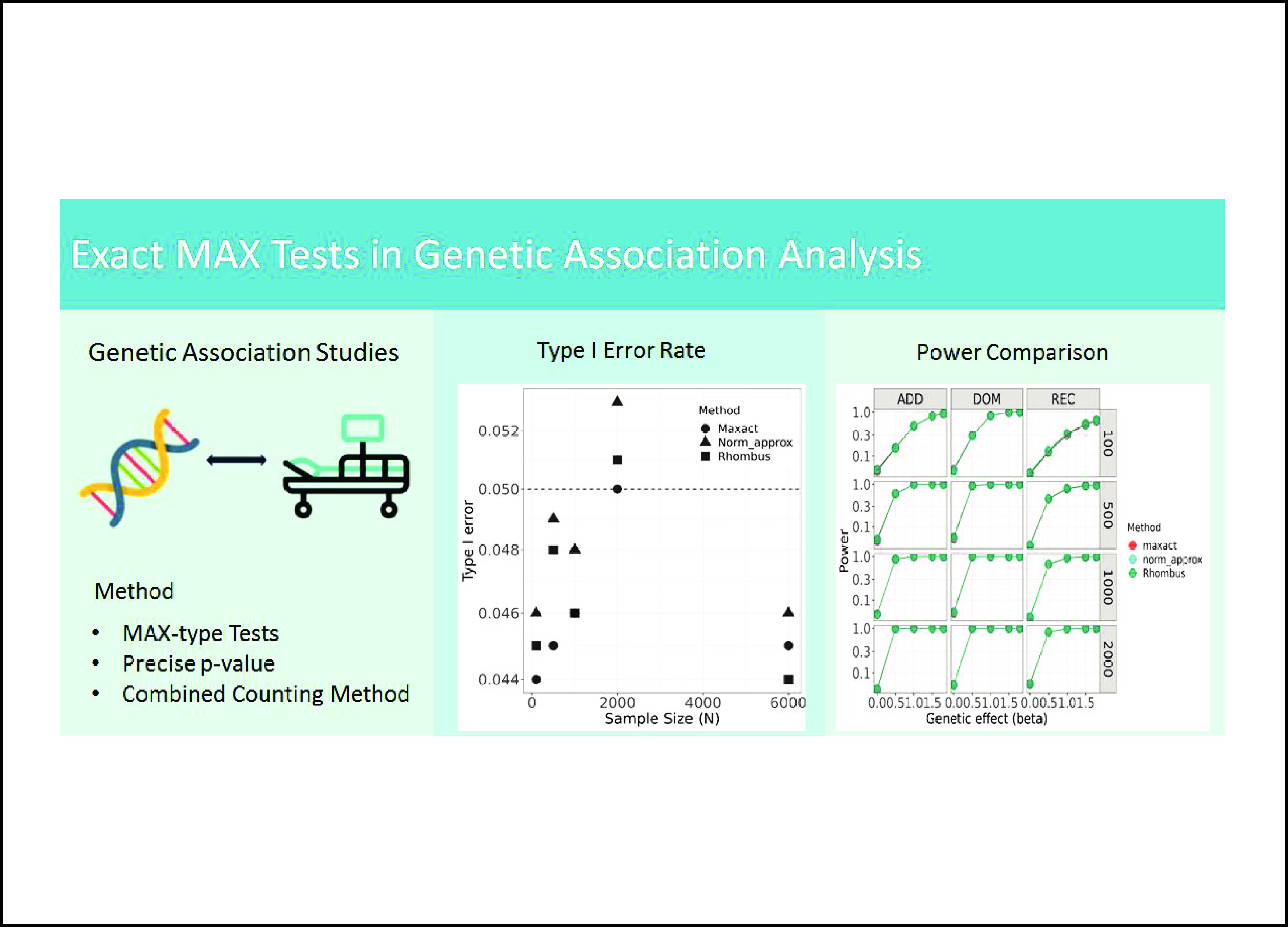
Type I error rate and power comparison of the proposed method MaXact, normal approximation, and Rhombus methods under various scenarios.
| [1] |
Armitage P. Tests for linear trends in proportions and frequencies. Biometrics, 1955, 11 (3): 375–386. DOI: 10.2307/3001775
|
| [2] |
Cochran W G. Some methods for strengthening the common chi-square tests. Biometrics, 1954, 10: 417–451. DOI: 10.2307/3001616
|
| [3] |
Sasieni P D. From genotypes to genes: Doubling the sample size. Biometrics, 1997, 53 (4): 1253–1261. DOI: 10.2307/2533494
|
| [4] |
Freidlin B, Zheng G, Li Z H, et al. Trend tests for case-control studies of genetic markers: Power, sample size and robustness. Human Heredity, 2002, 53 (3): 146–152. DOI: 10.1159/000064976
|
| [5] |
Balding D J. A tutorial on statistical methods for population association studies. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2006, 7 (10): 781–791. DOI: 10.1038/nrg1916
|
| [6] |
Zang Y, Fung W K, Zheng G. Tail strength to combine two p values: Their correlation cannot be ignored. American Journal of Human Genetics, 2009, 84 (2): 291–295. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.014
|
| [7] |
Zang Y, Fung W K, Zheng G. Simple algorithms to calculate asymptotic null distributions of robust tests in case-control genetic association studies in R. Journal of Statistical Software, 2010, 33 (8): 1–24. DOI: 10.18637/jss.v033.i08
|
| [8] |
Zheng G, Freidlin B, Gastwirth J L. Comparison of robust tests for genetic association using case-control studies. IMS Lecture Notes: Monograph Series, 2006, 49: 253–265. DOI: 10.1214/074921706000000491
|
| [9] |
Zhang J G, Liu L, Lin Z F, et al. SNP-SNP and SNP-environment interactions of potentially functional HOTAIR SNPs modify the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog, 2019, 58 (5): 633–642. DOI: 10.1002/mc.22955
|
| [10] |
Liu Q, Liu G Y, Lin Z F, et al. The association of lncRNA SNPs and SNPs‐environment interactions based on GWAS with HBV‐related HCC risk and progression. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine, 2021, 9 (2): e1585. DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1585
|
| [11] |
Yu H B, Hu W, Lin C W, et al. Polymorphisms analysis for association between ADIPO signaling pathway and genetic susceptibility to T2DM in Chinese han population. Adipocyte, 2021, 10 (1): 463–474. DOI: 10.1080/21623945.2021.1978728
|
| [12] |
Yu H B, Xu L, Liu H, et al. Association analysis of LEP signaling pathway with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han population from South China. BioMed Research International, 2021, 2021: 5517364. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5517364
|
| [13] |
Zheng G, Freidlin B, Gastwirth J L. Robust TDT-type candidate-gene association tests. Annals of Human Genetics, 2002, 66 (2): 145–155. DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-1809.2002.00104.x
|
| [14] |
Joo J, Kwak M, Chen Z, et al. Efficiency robust statistics for genetic linkage and association studies under genetic model uncertainty. Statistics in Medicine, 2010, 29 (1): 158–180. DOI: 10.1002/sim.3759
|
| [15] |
So H C, Sham P C. Robust association tests under different genetic models, allowing for binary or quantitative traits and covariates. Behavior Genetics, 2011, 41 (5): 768–775. DOI: 10.1007/s10519-011-9450-9
|
| [16] |
Zang Y, Fung W K, Cao S, et al. Robust tests for gene–environment interaction in case-control and case-only designs. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2019, 129: 79–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.csda.2018.08.014
|
| [17] |
Chen Z, Zang Y. CMAX3: A robust statistical test for genetic association accounting for covariates. Genes, 2021, 12 (11): 1723. DOI: 10.3390/genes12111723
|
| [18] |
González J R, Carrasco J L, Dudbridge F, et al. Maximizing association statistics over genetic models. Genetic Epidemiology, 2008, 32 (3): 246–254. DOI: 10.1002/gepi.20299
|
| [19] |
Li Q, Zheng G, Li Z, et al. Efficient approximation of p-value of maximum of corrected test with application to genome-wide association studies. Annals of Human Genetics, 2008, 72 (3): 397–406. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00437.x
|
| [20] |
Boulesteix A L. Maximally selected chi-square statistics for ordinal variables. Biometrical Journal, 2006, 48 (3): 451–462. DOI: 10.1002/bimj.200510161
|
| [21] |
Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature, 2007, 445: 881–885. DOI: 10.1038/nature05616
|
| AA | Aa | aa | Total | |
| Cases | r_0 | r_1 | r_2 | R |
| Controls | s_0 | s_1 | s_2 | S |
| Total | n_0 | n_1 | n_2 | N |
| Permutation replicates | Normal approximation | Rhombus approximation | |||||
| N | 10^3 | 5\times 10^3 | 10^4 | 5\times 10^4 | 10^5 | ||
| 100 | 1.229 | 0.538 | 0.392 | 0.179 | 0.121 | 8.438 | 9.048 |
| 500 | 1.294 | 0.563 | 0.392 | 0.180 | 0.124 | 3.232 | 10.587 |
| 1.313 | 0.570 | 0.381 | 0.183 | 0.127 | 2.256 | 10.971 | |
| 2000 | 1.315 | 0.558 | 0.411 | 0.184 | 0.129 | 1.577 | 11.366 |
| 1.301 | 0.598 | 0.428 | 0.184 | 0.130 | 0.843 | 11.748 | |
| N | MaXact | Normal approximation | Rhombus approximation | Permutation ( n=1 ) |
| 100 | 1.82 | 41.38 | 3.94 | 1.10 |
| 500 | 1.96 | 41.79 | 3.71 | 1.46 |
| 2.08 | 40.02 | 3.45 | 2.01 | |
| 2000 | 2.71 | 40.19 | 3.73 | 2.89 |
| 5.06 | 41.97 | 3.69 | 7.38 | |
| ^*Software: R; Computer: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU X5355 @ 2.66GHz. | ||||
| SNP | r_0 | r_1 | r_2 | s_0 | s_1 | s_2 | MaXact | Permutation (n \geqslant 10^8)^* | Normal approximation | Rhombus approximation |
| rs7900150 | 129 | 326 | 229 | 198 | 325 | 143 | 1.3 \times 10^{-8} | 1.3 \times 10^{-8} | 8.9 \times 10^{-9} | 1.4 \times 10^{-8} |
| rs7100927 | 129 | 328 | 229 | 198 | 326 | 143 | 1.3 \times 10^{-8} | 1.4 \times 10^{-8} | 9.0 \times 10^{-9} | 1.4 \times 10^{-8} |
| rs1193179 | 340 | 288 | 58 | 423 | 202 | 44 | 1.0 \times 10^{-6} | 9.8 \times 10^{-7} | 7.5 \times 10^{-7} | 1.0 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs932206 | 134 | 285 | 267 | 158 | 333 | 178 | 3.7 \times 10^{-6} | 3.7 \times 10^{-6} | 2.6 \times 10^{-6} | 3.7 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs1978717 | 300 | 308 | 75 | 364 | 260 | 36 | 4.0 \times 10^{-6} | 4.0 \times 10^{-6} | 3.0 \times 10^{-6} | 4.0 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs11084127 | 300 | 311 | 75 | 363 | 266 | 36 | 5.3 \times 10^{-6} | 5.2 \times 10^{-6} | 4.5 \times 10^{-6} | 6.1 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs1111875 | 77 | 298 | 310 | 122 | 316 | 231 | 7.8 \times 10^{-6} | 8.0 \times 10^{-6} | 5.2 \times 10^{-6} | 7.1 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs11084128 | 299 | 302 | 76 | 363 | 264 | 36 | 6.2 \times 10^{-6} | 6.3 \times 10^{-6} | 5.4 \times 10^{-6} | 7.2 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs282705 | 24 | 239 | 423 | 60 | 264 | 345 | 6.3 \times 10^{-6} | 6.2 \times 10^{-6} | 5.5 \times 10^{-6} | 7.3 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs1836002 | 300 | 311 | 75 | 364 | 268 | 37 | 9.2 \times 10^{-6} | 9.1 \times 10^{-6} | 6.8 \times 10^{-6} | 9.1 \times 10^{-6} |
| rs3740878 | 25 | 273 | 386 | 65 | 249 | 353 | 1.8 \times 10^{-5} | 1.8 \times 10^{-5} | 1.4 \times 10^{-5} | 1.8 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs11037909 | 25 | 274 | 387 | 65 | 251 | 353 | 1.8 \times 10^{-5} | 1.8 \times 10^{-5} | 1.4 \times 10^{-5} | 1.9 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs8101509 | 303 | 297 | 80 | 344 | 285 | 33 | 2.1 \times 10^{-5} | 2.1 \times 10^{-5} | 1.5 \times 10^{-5} | 2.0 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs2499953 | 646 | 39 | 1 | 660 | 9 | 0 | 6.3 \times 10^{-6} | 6.2 \times 10^{-6} | 1.9 \times 10^{-5} | 2.2 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs6670163 | 34 | 204 | 448 | 45 | 266 | 358 | 2.0 \times 10^{-5} | 2.0 \times 10^{-5} | 1.9 \times 10^{-5} | 2.5 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs945384 | 614 | 69 | 3 | 640 | 28 | 1 | 2.0 \times 10^{-5} | 2.1 \times 10^{-5} | 3.2 \times 10^{-5} | 3.8 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs1113132 | 25 | 271 | 390 | 63 | 251 | 355 | 3.9 \times 10^{-5} | 3.9 \times 10^{-5} | 3.2 \times 10^{-5} | 4.1 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs2278419 | 319 | 294 | 69 | 368 | 270 | 27 | 4.3 \times 10^{-5} | 4.1 \times 10^{-5} | 3.1 \times 10^{-5} | 4.0 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs7651936 | 156 | 326 | 204 | 186 | 351 | 131 | 4.4 \times 10^{-5} | 4.4 \times 10^{-5} | 3.1 \times 10^{-5} | 4.1 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs10211998 | 26 | 189 | 466 | 37 | 249 | 380 | 3.9 \times 10^{-5} | 4.1 \times 10^{-5} | 3.1 \times 10^{-5} | 4.0 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs5756371 | 28 | 194 | 462 | 41 | 251 | 376 | 4.0 \times 10^{-5} | 3.9 \times 10^{-5} | 4.0 \times 10^{-5} | 5.1 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs13064991 | 15 | 177 | 494 | 27 | 233 | 409 | 2.8 \times 10^{-5} | 2.8 \times 10^{-5} | 3.1 \times 10^{-5} | 3.9 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs1256517 | 471 | 184 | 17 | 527 | 116 | 15 | 5.2 \times 10^{-5} | 5.1 \times 10^{-5} | 5.0 \times 10^{-5} | 6.2 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs6541240 | 83 | 253 | 350 | 101 | 303 | 265 | 6.3 \times 10^{-5} | 6.2 \times 10^{-5} | 4.8 \times 10^{-5} | 6.2 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs6413504 | 126 | 340 | 215 | 185 | 313 | 163 | 7.0 \times 10^{-5} | 7.1 \times 10^{-5} | 5.1 \times 10^{-5} | 6.8 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs2050831 | 36 | 184 | 466 | 29 | 258 | 381 | 7.5 \times 10^{-5} | 7.4 \times 10^{-5} | 6.8 \times 10^{-5} | 8.7 \times 10^{-5} |
| rs873492 | 270 | 321 | 95 | 337 | 256 | 76 | 1.2 \times 10^{-4} | 1.2 \times 10^{-4} | 9.0 \times 10^{-5} | 1.1 \times 10^{-4} |
| rs11078674 | 297 | 304 | 83 | 354 | 267 | 46 | 8.0 \times 10^{-5} | 7.9 \times 10^{-5} | 5.6 \times 10^{-5} | 7.3 \times 10^{-5} |
| ^*n=10^{10} when p_3< 10^{-7} ; n=10^{9} when 10^{-7} \leqslant p_3< 10^{-5} ; n=10^{8} when p_3 \geqslant 10^{-5} . | ||||||||||