
ISSN 0253-2778
CN 34-1054/N
Isotropic magnetorheological elastomers (MREs) are smart materials fabricated by embedding magnetizable particles randomly into a polymer matrix. Under a magnetic field, its modulus changes rapidly, reversibly, and continuously, offering wide application potential in the vibration control area. Experimental observations show that there is a strong frequency, strain amplitude, and magnetic dependence of the dynamic behavior of isotropic MRE. Although important for potential applications, the magnetic-dependent nonlinear dynamic behavior of isotropic MRE has received little theoretical attention. To accurately evaluate the dynamic performance of isotropic MRE and to guide the design of isotropic MRE-based products, a new constitutive model based on continuum mechanics theory is developed to depict the magnetic-dependent nonlinear dynamic behavior of isotropic MRE. Subsequently, the numerical implementation algorithm is developed, and the prediction ability of the model is examined. The model provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanics of the magnetic-dependent nonlinear viscoelastic behavior of isotropic MRE. Furthermore, the model can be utilized to predict the magnetomechanical coupling behavior of isotropic MRE and therefore serves as a useful platform to promote the design and application of isotropic MRE-based devices.
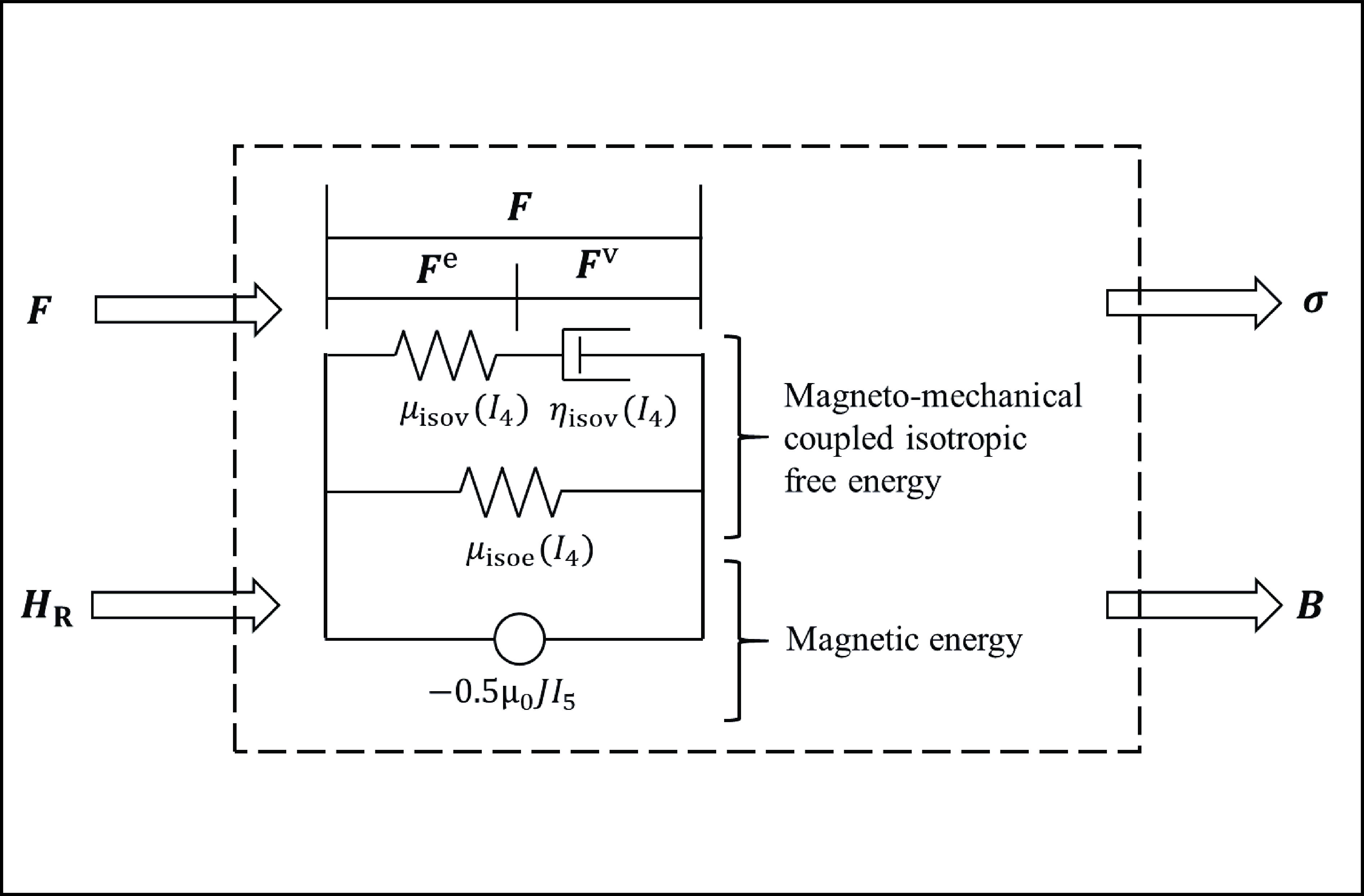
Schematical configuration of the magneto-dependent nonlinear dynamic model of isotropic MREs.
Figure 10. Comparison between experimental (Exp) and simulation (Sim) stress‒strain hysteresis results by the classical Maxwell viscoelastic model for isotropic MRE at zero magnetic field with different frequencies and strain amplitude. The lines and dots are experimental and simulation results, respectively.
Figure 11. Comparison between experimental (Exp) and simulation (Sim) stress‒strain hysteresis results by the classical Maxwell viscoelastic model for isotropic MRE at 0.4 T magnetic field with different frequencies and strain amplitude.The lines and dots are experimental and simulation results, respectively.
| [1] |
Blom P, Kari L. Smart audio frequency energy flow control by magneto-sensitive rubber isolators. Smart Materials and Structures, 2008, 17: 015043. DOI: 10.1088/0964-1726/17/1/015043
|
| [2] |
Alberdi-Muniain A, Gil-Negrete N, Kari L. Modelling energy flow through magneto-sensitive vibration isolators. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2013, 65: 22–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2013.02.003
|
| [3] |
Bastola A K, Li L. A new type of vibration isolator based on magnetorheological elastomer. Materials & Design, 2018, 157: 431–436. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.08.009
|
| [4] |
Deng H X, Gong X L. Adaptive tuned vibration absorber based on magnetorheological elastomer. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2007, 18 (12): 1205–1210. DOI: 10.1177/1045389x07083128
|
| [5] |
Wang Q, Dong X, Li L, et al. Study on an improved variable stiffness tuned mass damper based on conical magnetorheological elastomer isolators. Smart Materials and Structures, 2017, 26: 105028. DOI: 10.1088/1361-665x/aa81e8
|
| [6] |
Xin F L, Bai X X, Qian L J. Principle, modeling, and control of a magnetorheological elastomer dynamic vibration absorber for powertrain mount systems of automobiles. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2017, 28 (16): 2239–2254. DOI: 10.1177/1045389x16672731
|
| [7] |
Psarra E, Bodelot L, Danas K. Two-field surface pattern control via marginally stable magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter, 2017, 13 (37): 6576–6584. DOI: 10.1039/c7sm00996h
|
| [8] |
Psarra E, Bodelot L, Danas K. Wrinkling to crinkling transitions and curvature localization in a magnetoelastic film bonded to a non-magnetic substrate. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2019, 133: 103734. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2019.103734
|
| [9] |
Blom P, Kari L. The frequency, amplitude and magnetic field dependent torsional stiffness of a magneto-sensitive rubber bushing. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2012, 60 (1): 54–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2012.04.006
|
| [10] |
Bastola A K, Hossain M. A review on magneto-mechanical characterizations of magnetorheological elastomers. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 200: 108348. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108348
|
| [11] |
Nam T H, Petríková I, Marvalová B. Effects of loading rate, applied shear strain, and magnetic field on stress relaxation behavior of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomer. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2022, 29: 2984–2998. DOI: 10.1080/15376494.2021.1883162
|
| [12] |
Qi S, Yu M, Fu J, et al. Stress relaxation behavior of magnetorheological elastomer: Experimental and modeling study. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2018, 29 (2): 205–213. DOI: 10.1177/1045389x17730913
|
| [13] |
Jolly M R, Carlson J D, Muñoz B C. A model of the behaviour of magnetorheological materials. Smart Materials and Structures, 1996, 5: 607–614. DOI: 10.1088/0964-1726/5/5/009
|
| [14] |
Yu M, Xia Y Q, Yan X R. Analysis and verification on the chain-like model with normal distribution of magnetorheological elastomer. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2009, 22 (5): 545–550. DOI: 10.1088/1674-0068/22/05/545-550
|
| [15] |
Guo F, Du C B, Li R P. Viscoelastic parameter model of magnetorheological elastomers based on Abel dashpot. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 6: 629386. DOI: 10.1155/2014/629386
|
| [16] |
Li W H, Zhou Y, Tian T F. Viscoelastic properties of MR elastomers under harmonic loading. Rheologica Acta, 2010, 49: 733–740. DOI: 10.1007/s00397-010-0446-9
|
| [17] |
Wang B, Kari L. A nonlinear constitutive model by spring, fractional derivative and modified bounding surface model to represent the amplitude, frequency and the magnetic dependency for magneto-sensitive rubber. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 438: 344–352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsv.2018.09.028
|
| [18] |
Li R, Sun L Z. Dynamic viscoelastic modeling of magnetorheological elastomers. Acta Mechanica, 2014, 225: 1347–1359. DOI: 10.1007/s00707-013-1051-7
|
| [19] |
Fan J, Yao J, Yu Y, et al. A macroscopic viscoelastic model of magnetorheological elastomer with different initial particle chain orientation angles based on fractional viscoelasticity. Smart Materials and Structures, 2022, 31: 025025. DOI: 10.1088/1361-665x/ac4575
|
| [20] |
Leng D, Sun S, Xu K, et al. A physical model of magnetorheological elastomer isolator and its dynamic analysis. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2020, 31 (9): 1141–1156. DOI: 10.1177/1045389x20910272
|
| [21] |
Wang T, Zhu Z W. A new type of nonlinear hysteretic model for magnetorheological elastomer and its application. Materials Letters, 2021, 301: 130176. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130176
|
| [22] |
Dorfmann L, Ogden R W. Nonlinear electroelastic interactions. In: Nonlinear Theory of Electroelastic and Magnetoelastic Interactions. Boston, US: Springer, 2014: 91–112.
|
| [23] |
Danas K, Triantafyllidis N. Instability of a magnetoelastic layer resting on a non-magnetic substrate. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2014, 69: 67–83. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2014.04.003
|
| [24] |
Lefèvre V, Danas V, Lopez-Pamies O. A general result for the magnetoelastic response of isotropic suspensions of iron and ferrofluid particles in rubber, with applications to spherical and cylindrical specimens. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2017, 107: 343–364. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2017.06.017
|
| [25] |
Rambausek M, Mukherjee D, Danas K. A computational framework for magnetically hard and soft viscoelastic magnetorheological elastomers. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 391: 114500. DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2021.114500
|
| [26] |
Rambausek M, Danas K. Bifurcation of magnetorheological film-substrate elastomers subjected to biaxial pre-compression and transverse magnetic fields. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2021, 128: 103608. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2020.103608
|
| [27] |
Lucarini S, Moreno-Mateos M A, Danas K. Insights into the viscohyperelastic response of soft magnetorheological elastomers: Competition of macrostructural versus microstructural players. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 256: 111981. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2022.111981
|
| [28] |
Mukherjee D, Danas K. A unified dual modeling framework for soft and hard magnetorheological elastomers. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 257: 111513. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2022.111513
|
| [29] |
Haldar K. Constitutive modeling of magneto-viscoelastic polymers, demagnetization correction, and field-induced Poynting effect. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2021, 165: 103488. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2021.103488
|
| [30] |
Saxena P, Hossain M, Steinmann P. A theory of finite deformation magneto-viscoelasticity. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2013, 50 (24): 3886–3897. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.07.024
|
| [31] |
Wang B, Li Y, Gao Y, et al. The influence of particle chain-magnetic field spatial location, frequency, dynamic strain amplitude and the prestrain on the mechanical performance of anisotropic magneto-rheological elastomer. Polymer Testing, 2021, 104: 107411. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2021.107411
|
| [32] |
Reese S, Govindjee S. A theory of finite viscoelasticity and numerical aspects. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1998, 35: 3455–3482. DOI: 10.1016/s0020-7683(97)00217-5
|
| [33] |
Nguyen T D, Jones R, Boyce B. Modeling the anisotropic finite-deformation viscoelastic behavior of soft fiber-reinforced composites. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44: 8366–8389. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2007.06.020
|
| [34] |
Nedjar B. Frameworks for finite strain viscoelastic-plasticity based on multiplicative decompositions. Part II: Computational aspects. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 191 (15): 1563–1593. DOI: 10.1016/s0045-7825(01)00336-x
|
| [35] |
Olsen N B, Christensen T, Dyre J C. Time-temperature superposition in viscous liquids. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 86 (7): 1271–1274. DOI: 10.1103/physrevlett.86.1271
|
| [36] |
Williams M L, Landel R F, Ferry J D. The temperature dependence of relaxation mechanisms in amorphous polymers and other glass-forming liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1955, 77 (14): 3701–3707. DOI: 10.1021/ja01619a008
|
| [37] |
Yeoh O H. Some forms of the strain energy function for rubber. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 1993, 66 (5): 754–771. DOI: 10.5254/1.3538343
|
| [38] |
Eyring H. Viscosity, plasticity, and diffusion as examples of absolute reaction rates. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1936, 4: 283–291. DOI: 10.1063/1.1749836
|